A Land Surveyor is essential whenever you plan on building on property, or buying an already built commercial property. Many land surveyor have worked throughout our country history.
In fact, three of the four faces carved on Mount Rushmore are land surveyors (Presidents George Washington, Thomas Jefferson and Abraham Lincoln were all three surveyors, Teddy Roosevelt was not.).
Others popular names were Daniel Boone, Meriwether Lewis and William Clark (Lewis & Clark), Sir George Everest, Charles Mason & Jeremiah Dixon (of the Mason-Dixon Line fame) and author Henry David Thoreau practiced for a time in Concord, Alabama.
What is a Land Surveyor?
A land surveyor is a person with the academic qualifications and technical expertise to measure and plot the lengths and directions of boundary lines and the dimensions of any portion of the earth’s surface (including natural and other structures). That definition is quite a mouthful, but in actuality the field of surveying (geomatics) includes many other facets.
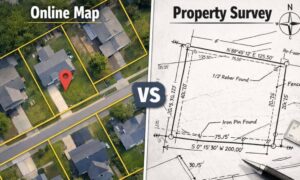
If you plan to purchase a lot, build your dream house, divide your property to your children, or simply want to know the details of a land property, a land surveyor is the best person to help you out. A land surveyor locates the boundary of your property and the location of your home within that boundary to determine if there are any encroachments by your neighbors onto you or vice versa. Common encroachments are fences, driveways, etc.
These days a land surveyor in the United States is regulated and licensed by the various state governments. In San Diego, the Board for Professional Engineers, Land Surveyors, and Geologists was established to protect the public. A land surveyor’s duty is “to safeguard life, health, and property, and to promote the public welfare by providing for the licensing and regulation of persons in the practices of engineering and land surveying. This purpose is achieved through the establishment of minimum qualifications for entry into the professions of engineering and land surveying, through the adoption of rules defining and delineating unlawful or unethical conduct, and through swift and effective discipline for those individuals or entities who violate the applicable laws or rules.”
How to become a land surveyor?
As of 2007, a newly licensed land surveyor is required to finish a four year degree in surveying or a closely related field, a four to eight years of on-the-job training under a licensed practicing surveyor. In addition to that, licensed land surveyors are mandated to attend 15 hours of continuing education annually to ensure that they are kept updated with the new know-hows that would help them on their professional growth.
What does a land surveyor do?
As part of a standard lot or mortgage survey of a property, expect your land surveyor to review tax maps, aerial maps, deeds, subdivision plats, zoning ordinances, subdivision regulations and possibly even flood maps. For a typical lot survey, the subdivision plat is the most important of these because it tells the exact dimensions of your lot and the relative location of your property corners. The surveyor uses this to locate and/or re-establish your property corners.
In the field, a land surveyor will search for your property corners along with some of your neighbors’ corners. If yours can’t be found, they’ll measure the distances and angles between all of the points, locate the improvements on your property, including your house, pool, out-buildings, retaining walls, fences, driveways, sidewalks, and other home improvements. Other improvements like sanitary sewer mains, storm drainage ways, overhead power lines and the like are located because these might indicate an easement across the property. The plat should show these, but may not in all cases.
Once all of the field information is gathered, the crew chief takes the field notes and prepares a preliminary sketch of the work. This is passed along to a draftsperson who prepares the final outline for your use. The draftsperson will check all of the maps mentioned earlier to make sure that all building setback lines and easements are shown on the draft. The surveyed distances and directions are compared to the plat distances and directions as well. Any discrepancies or encroachments are shown on the drawing. Your lawyer may use the draft to determine if any other legal work is needed during the closing. The mortgage company or the bank may also use the survey for their records.
So now, what do you have for your money. You have a drawing which shows your house on your lot. You should have stakes and/or flagging by all of your property corners. Make sure you know where they are located. The actual corner is marked by an iron pin or pipe of some sort. (The type of monument should be shown in your survey drawing.) You might also want to take a look at them at least once a year to make sure they’re still there. (Even animals mark their territory more often than that.)